SAP control system. What is SAP systems. Best SAP Books and Tutorials
In order for the business to develop in the best possible way, it is necessary to automate accounting at enterprises, regardless of their size and form of ownership.
It is also necessary for company leaders, who can quickly make corrective changes to achieve optimal performance.
To automate accounting at domestic enterprises today, there are many different proposals, such as:
- 1c accounting;
- Sail-accounting;
- BEST;
- Info-accountant;
Until recently, domestic enterprises used "1 C: Accounting". But since 1992, the German SAP program has been increasingly installed in large and medium-sized enterprises.
The clients of this software are such huge enterprises as joint-stock companies Gazprom and Gazprom Neft, Lukoil and TNK, Alrosa diamond company and many other giant corporations.
Video: App overview
What is the SAP program
The SAP accounting program is an automated system that allows you to plan the resources of large enterprises, which allows you to calculate everything to the smallest detail, and also forms a single information space.
Thanks to the modular principle on which the ERP system operates, it became possible to use not only individual components of the SAP system, but also their combination. 
Most maximum effect from using the system can only be achieved if the enterprise performs all operations in a single information environment. The SAP® ERP system allows you to immediately update and post the data that is immediately received by all the necessary departments of the enterprise.
The system uses a model consisting of three links:

The end user assumes that the accounting system has combined the main functions in two areas:
- reporting and accounting including everything you need. The program also takes into account internal production costs in all emerging places, allows you to manage orders and in cash, and also take into account all other results;
- logistics allows you to combine not only planning, but also management and sales, which include invoicing, further sales and shipments. Logistics also includes logistics, which allows you to make purchases, control invoices and manage inventory.
History of appearance
In 1972, a company was founded in Germany that creates software and providing consulting services for organizations. It was created by five employees of German origin who left the IBM Corporation.
The abbreviation of the company name is translated into Russian as " System Analysis and software development”. Quite quickly, she began to enjoy success and demand from the world famous companies, whose management was considered the most effective. 
From the very beginning, SAP has specialized in the development automated systems, which allowed to manage processes within the enterprise, these include not only accounting, but also production processes and trading operations. These also include personnel management and warehouse turnover.
The high quality of the product, constant innovation, and the ability to foresee have allowed SAP to become one of the four world leaders in the creation of programs used on the Internet since 2009. large enterprises.
Since 2007, the corporation began a merger, buying out companies that produce software for predictive analytics, analysis and data processing, controlling the quality and production processes at industrial enterprises and human capital managers. 
SAP develops a system whose applications adapt to the legal context of a given country. The company also helps to implement its system as additional services. To do this, she developed her own methodology, called ValueSAP.
most famous product
The most popular product is the ERP system, which allows you to manage all resources, both internal and external. It forms a single information space for entering, processing and receiving information about activities within the enterprise. 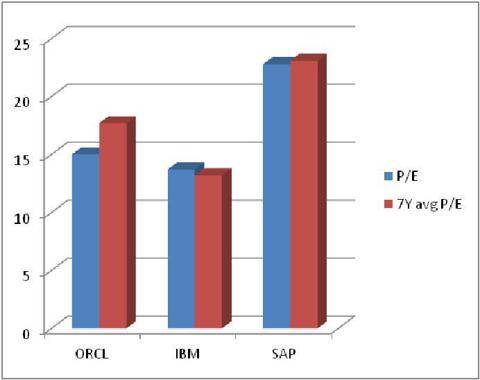
Thanks to the SAP R/3 product, designed as a comprehensive automation in large enterprises, the corporation quickly rose to the level of world leaders and became a world-famous software manufacturer that allows you to automate all procedures that form business processes.
In 2004, SAP introduced a software platform called SAP NetWeaver 2004, which included the following products:

Description of the SAP accounting program
SAP accounting software is installed only on enterprises big business, since the cost of software sometimes reaches 5% or 10% of the company's annual turnover, services for the implementation of the system are also quite high. And yet, no matter what, the largest corporations prefer to install this particular system. 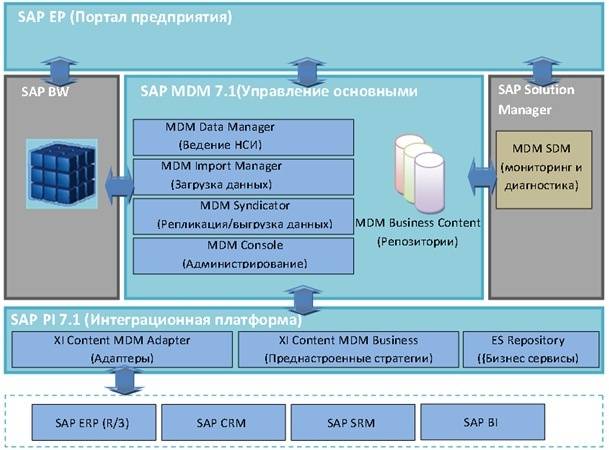
The functional areas of the SAP program consist of the following modules:

Additions to the package
Since the company is always looking to innovate, it has provided the following additions to the package:
- open PS is an add-on that serves as an interface between the Project System and other external systems. This add-on allows you to provide flexibility and freedom to access the necessary parts of the system from the outside, and also with its help you can perform important business operations;
- Internet and intranet- add-ons allow you to use corporate networks, automatically creating a login screen for each registered user. This allows you to increase the capabilities of the software by creating a supply chain management system that includes everything from customers to raw material suppliers.
Video: SAP ERP menu
Implementation stages
Implementation is a process that allows you to change the activities of the enterprise, while it must achieve its goals in a limited period of time.
Typically goals include:
- obtaining by management all the necessary information about the state of current affairs. The manager sees everything he needs almost in real time;
- Ranging, which is an improvement in business processes (unnecessary ones are eliminated, and efficiency is increased for useful ones).
Implementation stages include the following steps:

Best SAP Books and Tutorials
Despite the fact that the SAP program is extremely complex, many leaders of huge enterprises have appreciated it. The SAP system is not just a program, it helps to make decisions that allow you to change business processes, which in turn leads to a significant increase in profits.
Through innovation, SAP develops software products that can be used not only by large businesses, but also by medium and small businesses. On the SAP platform, Business One and Business All-in-One applications have been developed for them, which will fully satisfy their needs.
SAP Beginner's Guide
Version 1.08 from 10/27/2007
fatheryan.narod.ru with the help of the community SAPForum.com and other good people
“If you can’t explain something to a six-year-old child, then you don’t understand it yourself”
""BUT. Einstein""
Preamble. Who is it for?
For people who aspire to become consultants and don't know where to start. Initial knowledge in this area is small or completely absent, but there are brains and desire. The path to consultants for "programmers" and "subject specialists", of course, is different, the author tried to make the material understandable to everyone. In order not to expand the size of the document beyond any reasonable limits and not to bother beginners with all sorts of nuances, the author deliberately went to simplify many concepts (nevertheless, trying to avoid obvious mistakes). SAP courses and other sources of information are given in square brackets. The document is planned to be improved, I will be grateful for criticism and additions.
WARNING: Even if you learn this article by heart, this does not entitle you to call yourself a "SAP consultant". There are still thousands of pages of text ahead, and experience of working on the project is a must. All I can do is "put me on the right path". I wish you success.
What is the SAP R/3 system and why is it needed?
SAP R/3 is information system ERP (Enterprise Resources Planning - enterprise resource planning). The system is designed to automate all enterprise management activities: management and accounting, planning and much more. (By the way, lately it has been declared new concept based on the Netweaver platform: the system should not cover all areas, but provide services based on data from software products from different manufacturers. Whether it will take root, the future will show). The system is VERY large and VERY complex. Accept it as a fact: it is impossible to “put it on your computer yourself” and “figure it out over the weekend, in extreme cases, in a week.” Requests “give me a distribution kit, I will install it myself and figure it out” come in regularly, but they cannot have any other result than a waste of time. Although the author's experience is based primarily on R/3, most of the provisions of the article, with some care, apply to future versions of SAP.
How does all this work from a technical point of view?
A small program SAP GUI (Graphics User Interface - Graphical User Interface) is installed on the user's computer, the function of which is to display data received from the server and transfer user data and commands to the server (sometimes you can get by with an Internet browser instead of GUI).
server called a specialized powerful reliable computer designed to store and process data transmitted over a network of many users.
The server usually has Database Management System (DBMS)- a program designed to store data in the form of a set of interrelated tables, with the possibility of adding, changing, deleting and retrieving them (data) at the request of the user in various combinations. Access to the database (Database) is carried out, as a rule, using a special language SQL (Structured Query Language - Structured Query Language). In our case, in addition to the actual business data, the database stores all system settings, a repository (more on that below), and program texts in the ABAP/4 language.
Actually SAP The th is called the Application Server - a program running on the server that performs all actions on user data. Let's take a look at how it works with an example.
User vasya enters some number and presses Enter. The SAP GUI immediately communicates to the Application Server this number and the fact that the key was pressed. The Application Server requests from the database a part of the program in the ABAP/4 language, which must process the user's action, and starts executing it. An ABAP/4 program can, for example, extract some information from the database depending on the received number and then pass it to the SAP GUI for display to the user vasya.
What is the essence of the consultant's work and what is the implementation process?
Beginners (in any case, those whom I interviewed when applying for a job) often think that it is enough to install the program, well, maybe even train users, and "the process has begun." In fact, such a freebie takes place only when "implementing" very simple, narrowly functional programs with a small number of users, to which even the most primitive ERP system certainly does not apply.
An implementation project is a time-limited process of changing the activities of an enterprise, designed to achieve specified goals. The goals are usually:
Improve management awareness of current state affairs. The boss can see whatever he wants, almost in real time.
- Improvement (reengineering) of business processes (eliminating unnecessary ones, increasing the efficiency of useful ones). For example, before the introduction of the system, before issuing an invoice for the release of goods, the signature of the "inventory accounting department" was required in order not to try to issue something from the warehouse that is not there in the required quantity. When using a system where this data is available, and when issuing documents are automatically checked, this signature, together with the entire department, becomes unnecessary.
- Reduced management costs. Rarely achieved.
Consultants must achieve the specified goals within the specified time. For this you need:
Examine the activities of the enterprise (if this has not been done separately before).
- Develop and agree on proposals for its improvement.
- To achieve bringing the organizational structure to the required state.
- Train users (sometimes on projects, consultants do not teach users at all or only teach key users, and those, in turn, end users).
- To achieve competent and coordinated work of users to achieve the set goals.
- Adapt (configure) the system to the specifics of the client's business.
Of course, it is difficult for one person to implement all these functions, therefore, if possible, they are distributed between the project manager, business analyst and technical consultant (although in practice it happens that one person is "and the Swiss, and the reaper and ...").
Basic skills and knowledge of a consultant. What should and should not be done?
Based on the tasks described above, it is possible to formulate requirements for a consultant:
Good knowledge subject area.
- The ability to see the bad organization of work, figure out how to make it better, and convince people that you are right.
- Ability to teach.
- Knowledge of the capabilities of the system, the business logic embedded in it and the limits of its adaptation.
- Ability to customize and modify the system for the client.
- Ability to correctly formulate solutions and requirements and document them.
- Communication skills.
- Ability to properly plan your time.
- Organizational skills.
- Ability to solve non-trivial problems.
DO NOT try to automate a "crooked" business, because:
1) tormented with the adaptation of the system;
2) will still have to be redone later.
As you know, if you automate a mess, you get an automated mess, which is a hundred times more difficult to clean up than usual. Accordingly, one of the most valued skills of a consultant is the ability to "upset" a zealous user (a standard example: "I want everything in this SAP of yours to be like in 1C, otherwise I will not work in such a system") and find compromises.
What is an SAP transaction?
SAP transaction- an application program that performs a business process in the system, performing a certain logically complete set of actions on data. (Technically, this is a "shortcut" for calling an ABAP/4 program). For example, it can be the input and accounting posting of an invoice, the formation of some report. (Programmers: SAP transaction is not synonymous with DB transaction).
What are modules?
The system is logically divided into modules. Each module consists of a set of transactions covering a certain part of the enterprise's activities. As a rule, the consultant specializes in a particular module (although the narrowness of the horizon has never led to anything good, so if possible you should not artificially put yourself in a box). The boundaries of the modules are largely conditional, data is exchanged between them, there may be common settings and tables with data, sharing the same part of the program on ABAP / 4 (with all the ensuing consequences if it is ill-considered changing).
Brief description of modules.
MM(Materials Management) - Management of material flows.
Includes:
1) Accounting in terms of accounting for stocks in warehouses, movement and write-off of goods and materials (inventory).
2) MRP (material requirements planning)
3) Reference book of materials
4) The procurement system starting from the application and ending with the receipt of goods and materials at the desired warehouse.
Receives data from the maintenance module (PM). If MRP is set up, requisitions for goods and materials are generated from maintenance orders.
The generated postings are transferred to FI.
When selling to a third party, part of the operations (for example, invoicing) can be implemented using SD (sales).
FM – Budget management. Other names FI-FM, PSM-FM. There is a second more modern version of the BCS module - the Budget Management System.
The purpose of both FM and BCS is management accounting, and if in a simple way - in what areas (budget items) the money was spent by accounting entries.
If all the budget money has already been spent, the system prohibits making postings (well, or it warns about problems with the budget).
Data for FM is taken from MM, FI, CO, SD, TORO (but not necessarily all at once).
Basis occupies a special place among other modules.
Basisniks are responsible for the functioning of SAP (application server) as a whole. Tasks:
Initial installation and performance tuning.
Database administration.
Installation of update packages and proofreading (notes).
Implementation of transfers (transports) to a productive system.
Administration (input and assignment of roles) of users.
Backup data.
Setting up the interaction of systems (data transfer between systems).
Monitoring (control) of the system in order to identify problems in advance and take measures.
Configuring access to systems by SAP support.
Keeping system data up to date at service.sap.com
Providing access (issuing a name, password and authority) to work with the SAP service.
Dump analysis (preferably together with functionalists - consultants on application modules and abapers).
The enumeration is incomplete, but I think it is sufficient for understanding. By the nature of his occupation, the manager has full authority in the system (SAP_ALL). Any mistake can easily lead to a complete collapse of the system. In this regard, the basis manager must have both deep knowledge and colossal responsibility and self-discipline. In addition, this is the most conservative person in the team - he is against all kinds of experiments, installing untested updates, etc.
For the productive development of a business, it is necessary to have control over all stages of production, accounting accounting. Thanks to this, the company will be able to quickly respond to changing factors and adapt to the situation.
As one of the means to achieve automation is SAP software. The abbreviation stands for System Analysis and Program Development or System Analysis and Program Development.
How SAP works
On the Russian market compete several programs for accounting, some of which do not require special skills and knowledge ( Microsoft Office Word, Excel), while others need a specialist:
- 1c accounting;
- Galaxy;
- Sail;
- Microsoft Dynamics Axapta.
SAP has many possibilities and even more features:
- automation of the work of an accountant;
- trading operations;
- warehouse operations;
- personnel accounting;
- financial accounting;
- accounting for the value of shares;
- drawing up payroll schedules;
- handling logistics and more.
The structure of the program is extremely complex, so only a trained person can deal with it. The salary of such workers is appropriate: in European countries, the administrator receives from 2500 €.
SAP program speeds up data processing and indicates the optimal course that the company should be guided by, however, the program will not be productive if the structure of the company itself has illogicalities, and its components are poorly interconnected. 
The functionality of the program is wide and consists of modules.
| Module | Title in Russian | Module Features |
| PP | Production planning. | Planning and management of production and its cycles. |
| MM | Management of material flows. | Managing production facilities:
|
| PM | Maintenance. | Repair and maintenance of the property of the enterprise and its equipment. |
| SD | Sales. | Invoicing, processing orders and offers. |
| AM | Fixed asset management. | Processing of enterprise property states:
|
| AA | Tax flows | Calculation of payment of taxes. |
| FI | Finance. | Financial control and full accounting reporting:
|
| HR | Personnel Management. | Work with personnel:
|
| CO | Control. | Management accounting and full control over the structure of production:
|
Company formation
The creator of the program was German company developers, spun off from IBM. This happened in 1972, and since 1992, accounting software products began to change in favor of SAP at medium and large enterprises. By 2003, SAP was almost completely ousted from the market competitors in Europe and the CIS due to its reliability, high-quality implementation and multifunctional support.
In 2006, courses began to appear to teach the features of the program. However, in the CIS countries, the 1C system is still used in small firms, as it is more convenient to use for untrained employees. Enterprises like Gazprom, Lukoil and Alros use SAP.
The creators of the program specialized specifically in helping companies, so SAP can be fully customized by the programmer individually for the needs of the company.
Advantages and disadvantages of the software package
The SAP system has a number of advantages, including:

To disadvantages can be attributed:
- High cost. Installation and implementation cost up to $1 million. In addition, it is necessary to train employees and pay salaries to the administrator and programmer. Customizing the program for the needs of the company is also expensive.
- Inability to install another program, since the contract is for a certain period. Termination of the contract will bring losses.
- Poorly implemented translation into Russian.
Most Popular Packages

SAP software has a lot of packages, each of them is customized for specific needs. Most often install SAP ERP, or SAP R / 3. This package plans the resources of the enterprise, external and internal. It is convenient because it works in real time. Up to 50% of all global companies work on the ERP system.
SAP also has following packages:
- Process Integration (PI). Solutions for integrations of various levels.
- Enterprise Portal (EP). Solution of portal tasks.
- Mobile Infrastructure (MI). Assistant in the implementation of mobile applications.
- Business Intelligence (BI). Assistance to business analysts.
- Knowledge Management (KM). Assistant to control educational programs.
- Master Data Management (MDM). A system for maintaining reference information, as well as regulations.
Program implementation
The introduction of SAP (customization of the program to the needs of the company) in the company takes place in 4 major stages.

Software add-on
The SAP Developer Corporation has a lab that releases updates and introduces new features and packages. But enterprises are not always willing to buy new packages because of their high cost, so additional software has been created, that is, additions to the main package.
Additional software allows you to expand the range of SAP capabilities, make the package more flexible.
open PS
This add-on provides access to the SAP system outside the computer on which it is installed. With it, it is also possible to perform various operations remotely.
Intranet
The add-on creates an account for each user, and also gives him an interface. The system can include suppliers, customers, managers, etc.
Business Add-Ins (BAdIs)
Checks reporting, proposals, documentation for relevance and reliability. It also allows you to determine the cost of a product or its batch.
All systems that implement accounting and planning in various areas of the enterprise, the SAP ERP system has a modular structure. At the same time, the architecture and capabilities of the modules are quite different from each other.
From the point of view of automated business processes, I would classify the components into several functional sections:
- Finance and Accounting
- Controlling
- Logistics
- Personnel Management
- Basis
- Industry Solutions
- Additional tools that automate business
In turn, the functionality of the above sections is implemented by the system modules, while the relationship of any module to a particular section is very conditional, since the modules are often deeply integrated and often simultaneously implement various functions.
The composition of the system modules:
Section "Finance and Accounting"
- FI - Finance (it would be more correct, of course, to identify FI with the section, but historically in Russia it so happened that in the section "Finance and Accounting" the FI module itself is separated from its component parts, such as, for example, FI-AA - "Accounting for fixed assets ”, FM - “Finance”). This module implements enterprise accounting. And, as I wrote earlier, there are functions of both reflecting the fact and planning. It includes: general ledger, Accounts receivable, Accounts payable.
- FI-AA - Asset Accounting. The module is deeply integrated into FI (which is understandable in principle), and also "seamlessly" spliced with the PS "Project System" module, which makes it possible to build a powerful capital construction management solution. Of course, integration with other modules is also possible, but more on that later.
- FI-FM (the module is usually called that, although PSM-FM is correct) - Financial management, Budget, Financial Management, etc., as soon as this module is not named, but all because SAP AG offended it with the name. Previously, this module was called FI-FM (FM - Fund Management), i.e. fund management. Then it was called PSM-FM (Public Sector Management - Fund Management), if you literally translate it, you will agree that it does not have anything to do with the fact that this module is usually used to form and control BDDS in an enterprise.
- FSCM - Value Chain Management. Not so long ago, separated into a separate module, it is a prefabricated hodgepodge, which was assembled from previously existing modules and remakes. Currently, only one functionality is popular - financial and risk management, accounting is implemented on this component valuable papers, credits and loans, deposits. And so the set of components is very extensive: Credit Management (defector from the SD "Sales" module), Biller Direct, Cash and Liquidity Management (old component, does not meet any customer requirements, do not be fooled by the name), Collection Management, Duspute Management, Internal Cash (here also the name does not correspond to the content in any way, the functionality is aimed at organizing within the framework of a holding likeness of an internal bank - it is debatable in relation to the legislation of the Russian Federation), Financial and risk management (here, there is a functionality for accompanying financial transactions).
- IM - Investment Management. Also a great outdated and not developing module. It is aimed at building the investment program of the enterprise, works in tight coupling with other modules, such as PS - project system, CO - controlling, PM - technical management. maintenance and repair of equipment. Currently being gradually replaced by the RPM (Resource and Portfolio Management) product.
- RE - Real estate management. Allows you to manage property, from a banal registry, to the maintenance of lease agreements, etc.
- FI-BL - Banks. The module is designed to work with banks.
The next section is "Controlling"
- The CO module itself is controlling. Probably the most flexible of all system modules. Solves the issues of planning and managing the economy of the enterprise. Deeply and seamlessly integrated into almost all modules of the system.
- PS - project system. In theory, all the other modules that I refer to the Controlling section are actually some add-ons on the CO module. Along with new features, unfortunately, they also differ from CO in a loss of flexibility. PS is intended for project management, in the system it is most often used to manage capital construction or to manage unique production (although for capital construction it's still better sharpened).
- PP - production planning. Here, even by the name it is clear that this module is designed to control production process. The module has many extensions that go beyond the scope of the ERP system, for example for capacity balancing. The functionality of the module solves the problems of serial as well as continuous production quite well.
- PM - management of TORO (maintenance and repair of equipment). The module is very popular, it allows you to solve the problems of planning repairs, monitoring equipment (by entering readings into the system control devices), costing for repairs, etc.
Section "Logistics"
- MM - material flow management. Planning the need for materials and services (including integration with other modules, for example: CO, PS, PM, PP, etc.); arrival at the warehouse, movement, warehouse accounting, invoicing, etc. This module, probably on a par with FI, is the most common and well-developed in terms of implementing management requirements.
- SD - sales management. Sales automation tasks are solved here: customer ranking, pre-sales work, customer order processing, delivery support, invoicing (preparation of documents: invoices, waybills, etc.).
Section "Human Resource Management (HCM)"
- HCM-PA - Human Resources. Automation of all basic personnel accounting processes.
- OM- organizational management. Automation of enterprise structure management, staffing, etc.
- TM - Time management.
- PY - calculation wages. A very flexible module, perhaps also due to the fact that a special tool is built into it, which, by writing various scripts, allows you to implement any calculations.
It is recommended to install the components of this section on dedicated servers, which is natural considering the data they work with. But at the same time, a certain paradox arises, since in SAP ERP, for example, working with staffing and user permissions are very convenient to implement using HCM tools (this is not necessary, but very convenient), also taking into account working hours. Therefore, some data must be synchronized in two systems: the main ERP system and the HR system, and this complicates and increases the cost of implementing this component.
Basis
Any system requires administration, the functionality of the BASIS section is aimed at ensuring operability, optimizing performance, maintaining changes (this function is implemented especially well), maintaining users and permissions, etc. Separately, it is necessary to highlight the possibility of developing in the ABAP / 4 language, in which, in principle, all the functionality is written. It enables the implementation of functions not implemented in the system standard, as well as its modification.
Industry Solutions (IS)
Listing industry solutions is a thankless task, I will note only one of them.
IS-U - management of transportation and marketing services for energy resources and housing and communal services. It is mainly used for electricity billing, but there are implementations in heat billing as well. Solves tasks:
This industry decision, when implemented, has a strong impact on the system, especially on the FI module, because forces to use a fundamentally different method of accounting, the so-called checking accounts, which is very different from the classical solutions.
Additional tools
The system has a number additional tools, with the help of which business automation tasks are solved. The functionality implemented using some of them is already a system implementation standard:
DMS- Document management system. This simple tool was originally designed in the system for storing scanned copies of original documents and other files with the ability to link to system objects. But due to the flexible interface (flexible not without the help of ABAP development) and the built-in status system, it is very often used for automation contract work, DSM documents are used as electronic contract cards.
RCM– to replace DMS, currently coming New Product- Corporate content management. It differs from DMS in an even more flexible interface, the ability to maintain templates, a built-in approval system (although it is possible to tie a approval system to DMS), etc.
WF (workflow)- a tool that allows you to implement electronic approval, notification, etc. In fact, this tool also underlies the coordination in the RCM module. As such, this tool is not self-sufficient, but rather applied, because. works with objects of other modules. But the tool is very powerful and flexible, so it was impossible not to say about it.

